by Andrew Korybko
Catalonia’s separatist campaign has dominated European headlines for the past couple of weeks, but it’s really the northern Belgian region of Flanders which will serve as a barometer over whether large chunks of the EU will fall apart into a collection of identity-centric statelets prior to the bloc’s reconstitution into a “federation of regions”.
What’s going on in Catalonia is of paramount importance to the geopolitical future of Europe, since it could very well serve as the catalyst for fracturing the EU if copycat movements elsewhere are emboldened by the Spanish region’s possible separatist success. This was explained in detail in the author’s recent analysis about “The Catalan Chain Reaction”, which readers should familiarize themselves with if they’re not already acquainted with the thesis put forth in that work. To concisely summarize, there’s a very distinct possibility that the EU’s liberal-globalist elite have been planning to divide and rule the continent along identity-based lines in order to further their ultimate goal of creating a “federation of regions”.
Catalonia is the spark that could set off this entire process, but it could also just be a flash in the pan that might end up being contained no matter what its final result may be. Flanders, however, is much different because of the heightened symbolism that Belgium holds in terms of EU identity, and the dissolution of this somewhat artificially created state would be the clearest sign yet that the EU’s ruling elite intend to take the bloc down the direction of manufactured fragmentation. Bearing this in mind, the spread of the “Catalan Chain Reaction” to Belgium and the inspiration that this could give to Flanders to break off from the rest of the country should be seen as the true barometer over whether or not the EU’s “nation-states” will disintegrate into a constellation of “Balkanized” ones.
“The First Bosnia”
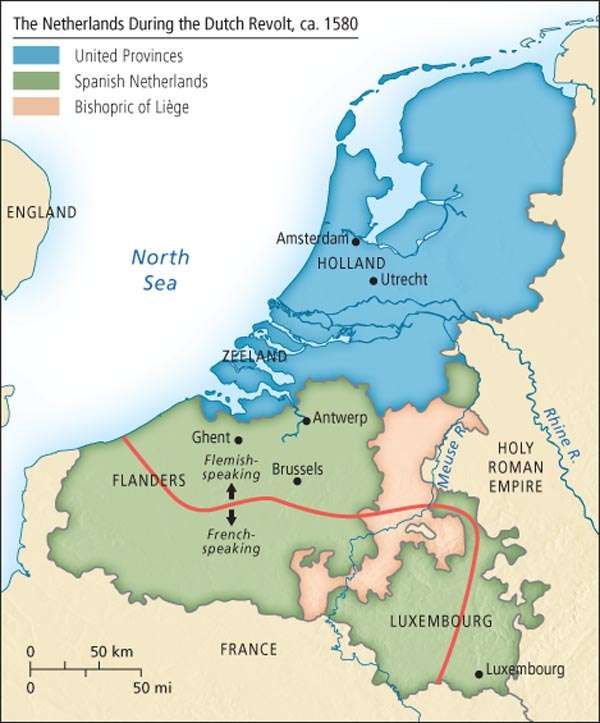
In order to properly understand the state of affairs at play, it’s necessary to briefly review the history of what could in some sense be described as “The First Bosnia”, or in other words, Europe’s “first artificially created state”. Most of the territory of what is nowadays referred to as Belgium was unified with the modern-day Netherlands from 1482-1581 when the political entity was referred to as the Habsburg Netherlands. The southern part (Belgium) came under Spanish control from 1581-1714 when it was called the Spanish Netherlands. Afterwards, it passed under Austrian administration from 1714-1797 when it became the Austrian Netherlands prior to its brief incorporation into the First French Republic and later Empire from 1797-1815. It was during the Spanish and Austrian eras that Belgium began to consider Catholicism as an inseparable part of its national identity in opposition to the Netherland’s Protestantism. Finally, Belgium was part of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands from 1815-1839 until the Belgian Revolution made it an independent state for the first time in its history.
In essence, what ended up happening is that a majority-Catholic but ethno-linguistically divided population got caught up in the 19th century’s wave of nationalism and created a hybrid Franco-Dutch state that would eventually federalize in the late-20th century, in a structural sense serving as a precursor to the dysfunctional Balkan creation of Bosnia almost a century and a half later.
It’s important to mention that the territory of what would eventually become Belgium had regularly been a battleground between the competing European powers of the Netherlands, the pre-unification German states, France, the UK, and even Spain and Austria during their control of this region, and this new country’s creation was widely considered by some to be nothing more than a buffer state. The 1830 London Conference between the UK, France, Prussia, Austria, and Russia saw the Great Power of the time recognize the fledgling entity as an independent actor, with Paris even militarily intervening to protecting it during Amsterdam’s failed “Ten Day’s Campaign” to reclaim its lost southern province in summer 1831. For as artificial of a political construction as Belgium was, it fared comparatively well during the 19th century as it leveraged its copious coal supplies and geostrategic position to rapidly industrialize and eventually become a genocidal African colonizer in the Congo. Although it was devastated in both World Wars, Belgium was able to bounce back in a relatively short period of time, partly because it could rely on its Congolese prison state.
Continue: Forget Catalonia, Flanders Is The Real Test Case Of EU Separatism! – OrientalReview.org